Atomic Symbol: Ar
Atomic Weight: 39.948
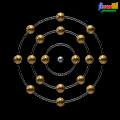
Electron Configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p6
Boiling Point in Kelvin: 87.29
Atomic Radius in nM: 0.174
1st Ionization Energy in kJ/mole: 1520.4
HISTORY
Argon is the first noble gas to be discovered. Although its presence in air was suspected by Cavendish in 1785, it was found in 1894 by chemist William Ramsay. Ramsay was working under Lord Rayleigh, a professor of physics at the University of Cambridge in England, who was studying the density of nitrogen gas. Through experiments, Lord Rayleigh found that nitrogen separated from ammonia (NH3) had a density of 0.5% less than that of nitrogen found in the air. He didn’t know why, so Ramsay decided to investigate.
Ramsay removed the oxygen and nitrogen from a quantity of liquid air through fractional distillation. He found that there was a small residue of gas left. He put this residue in a glass tube and electrically excited it. When he studied the excited gas with a spectroscope, Ramsay discovered a new pattern of lines. Oddly, there seemed to be no place in the Periodic Table for a new gaseous element.
In 1894 Ramsay had the idea for a new column of elements. He thought that this gas was the first member. Ramsay named this new element “argon,” for the Greek argos, meaning “lazy,” or “inactive.” Ramsay thought it was lazy because it seemed to have no chemical properties.